What is the difference between Corn and Wart?
If you are looking for the answer to what corn is on foot, then pay attention to this article. I will guide you about the wart medication, corn medication and the complete pathogenesis of Wart forming.
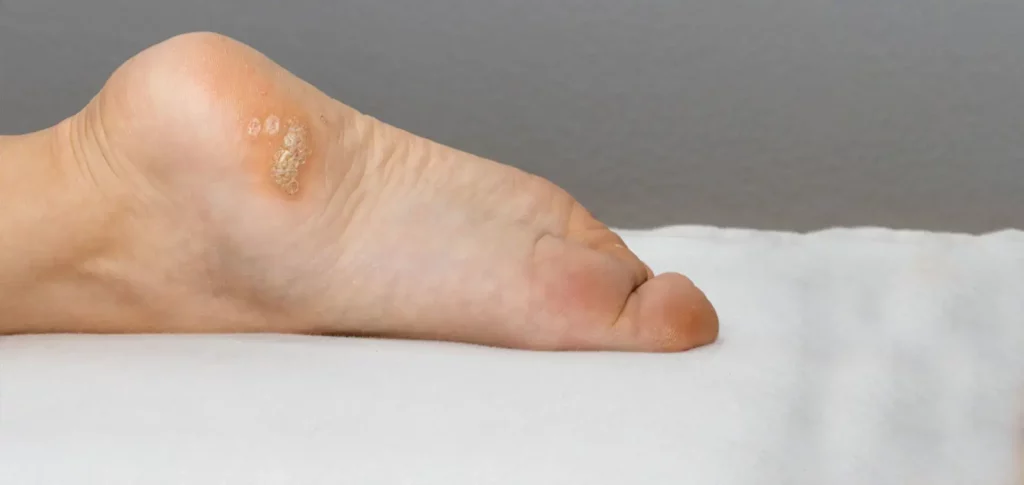
Corn vs Wart
Corn vs Wart on feet are two different diseases of the foot. Warts are benign skin growth, whereas corn arises due to Constant friction pressure. Corn is also called helomas that develop by wearing tight shoes. They are usually multiple hyperkeratotic skin patches with finger-like projections, common during 10-20 years of age. Dear readers, This article is properly medically reviewed, and certain references to the book have been given at the end of the article.
| Corn | Wart |
| Corns are Thickening of Areas of skin. | Wart are Hyperkeratotic, pearly white skin patches. |
| These are caused by constant pressure. | They are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). |
| These are neither familial nor viral. | Wart can be familial and viral. |
| These are not contagious. | Wart can be transmitted from one person to another sexually or by kissing. |
| Location: Corn on the side or top of the foot. | Location: Wart on heels, under the surface of the head of the first metatarsal bone, hands, finger, and face |
| Corn remover Vs wart removals are two different approaches. | These are treated with an immune modulator, laser, or cryotherapy. |
| These are treated by foot pads, removing the source of friction or pressure. | They require surgical intervention. |
What is a wart?
Warts are non-malignant growths of skin, mucosa, and epithelium. These are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) type 6 & 11. They are common in fingertips, face, axilla, palms, and soles. The Wart can attain its size within a week and persist for years. Warts are oval-shaped, rough, raised skin lesions with Central HPV black spots, especially black spots on the heel of the foot. The presentation of corn versus Wart on the bottom of the foot is slightly different.
Types of warts:
Verruca Vulgaris (common warts)
Skin bumps on fingers and Sole due to infective HPV. They are flesh-coloured lesions with rough skin covering.
Verruca Plantaris (Plantar Warts)
It gets pushed into the sole of the feet due to walking. It is more common on the Heel and head of the first metatarsal bone. It is pearly white with haemorrhagic flecks. It is covered by normal skin due to Deep invagination. Plantar warts are multiple and painful.
Flat Warts
These are smaller in size with smooth skin surfaces. They appear on the face, neck and hand. They are pink or yellowish.
Filiform Warts
They appear as finger-like projections on the face near the mouth, nose and eyes.
Periungual warts
These lesions affect nails. They affect the growth of nails by damaging the base of nails.
Genital Warts
They are also called condyloma acumimata. They are sexually transmitted and have multiple pedunculated, papilliferous skin excrescences that resemble. These anal warts are carried by 20% Population.
Butcher wart / Pathologist wart/ Verruca Necrogenica
These are mostly on the dorsum of the hand of milkmaids. The causative agent of this type is mycobacterium tuberculosis, which gets entry through broken skin. It presents as a Bluish lesion from in which fluid oozes and is surrounded by pustules.
Senile warts
These are harmless brown-coloured warts spotted during adult life. They show signs of skin ageing.
What is a corn on foot?
Corns or helomas are thickened skin patches. These are due to repeated soft tissue friction between Bone and hard corn shoes. If we research corn vs. Wart on hand/ corn vs. Wart on fingers, then corn is treated spontaneously if the source of friction or pressure is removed.
Types of Corns
Hard corns
These are the most common types of Corn. There were on type and side of feet. They consist of a thick, dense core of skin covered by a hard area.
Soft Corn
That develops between toes where the skin is sweaty and moist. They are white in color and rubbery in nature. Mostly, clinicians confuse it with tinea pedis.
Seed corn
They are tiny, painless, and multiple pebble-like lesions on the bottom of the feet.
Vascular Corn
They are brown to black due to blood vessels within the skin lesion. They are tender and can bleed on touch.
Fibrous Corn
That wealth on the weight-bearing area of feet. These present a skin lesion covered with a thick collagenous cap.
Neurovascular Corn
They develop on loony prominence and are height tender.
Signs and Symptoms
Sign and Symptoms of foot corn versus wart is slightly different. Both are raised, rough skin lesions that can be painful. Corn has central hollowness; therefore, it can be compressed to deeper layers, whereas Wart cannot. Warts are cauliflower-like papules or plaques of Skin, whereas corns are thickened skin with a central core of Hollowness.
Diagnosis
You can diagnose any disease by following a given Pattern.
Corns vs Warts on Feet Treatment
Treatment has two different approaches. You can treat foot corn vs. Wart in different ways.
| Treatment of corn | Treatment of warts |
| Use well-fitted shoes (canvas shoes). | Topical treatment by using imiquimod. |
| Foot pads. | 5- Fluorouracil |
| Exfoliate the affected skin. If all the above measures fail, corn can be surgically removed under proper aseptic conditions. | Podophyllin |
| Cushioning Pads: Over-the-counter, non-medicated corn pads or cushions can provide a barrier between your foot and the shoe, reducing friction and pressure on the corn. | Laser therapy |
| Salicylic Acid: Over-the-counter salicylic acid treatments come in the form of pads, plasters, or solutions. These products work to soften the corn and help it gradually slough off. | Cryotherapy |
| Soaking and Exfoliation: Soaking your feet in warm water can help soften the corn, making it easier to exfoliate with a pumice stone or an exfoliating scrub gently. Be gentle and avoid over-exfoliating, as this can lead to irritation. | Surgical excision of wart. |
Pathogenesis of wart
Pathogenesis of any disease means knowing about the development process of any illness. Verruca vulgaris is caused by viral infection. The causative agent HPV type 6 & 11 Infect skin basal cells that lead to Cellular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis. Both types of HPV have circular DNA.
Pathogenesis of corn
Corn is formed by repeated friction of skin between two Hard surfaces. It can also lead to periosteal stimulation that causes abnormal bone growth.
What causes warts and Corn?
Human papillomavirus type six and type eleven are transmitted through broken skin or Sexual contact and cause the development of verruca Vulgaris. Corn develops due to repeated or continuous friction or pressure by wearing tight shoes, abnormal walking style, and rough surface.
Risk factor
Risk factors of verruca vulgaris include HPV infection, trauma, bare feet walking, and familial transmission. Risk factors of corn are tight shoes and repeated pressure over the side and top of the sole or finger.
What is the removal procedure like?
The removal procedure of both was and Corn are similar.
Are Corn and warts the same thing?
No, they are different diseases. They present in a slightly similar fashion. A good Clinician can differentiate among the twos by taking proper history and doing clinical examination.
